Un diccionario, o mapa, consiste en una colección de pares clave-valor. La clave se utiliza para acceder al valor asociado. Las claves deben ser únicas dentro de un diccionario. Los valores pueden repetirse.
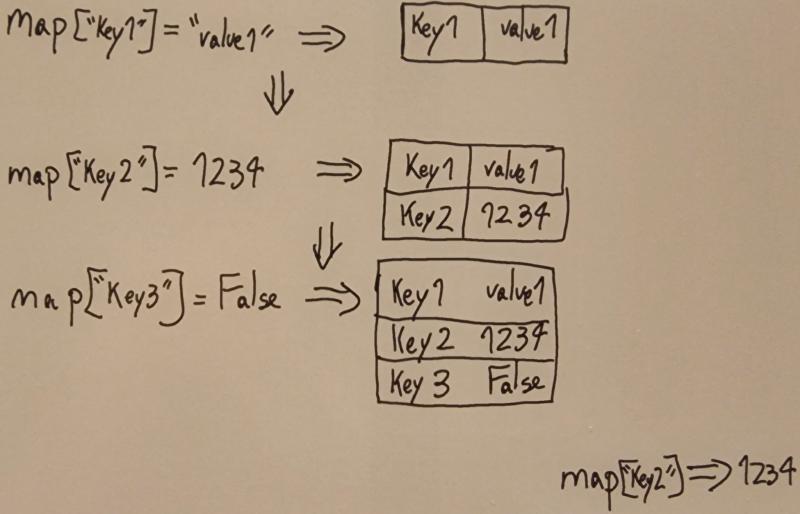
Operaciones principales#
- Añadir/actualizar: Inserta un par clave-valor. Si la clave existía, su valor es reemplazado.
diccionario['clave'] = 'valor' - Obtener valor: Acceder al valor dada una clave.
valor = diccionario['clave'] - Eliminar: Remueve un par clave-valor del diccionario.
del diccionario['clave'] - Recorrer: Iterar sobre las claves, valores o pares del diccionario.
for clave in diccionario: print(clave, diccionario[clave]) # clave, valor
Creación de un diccionario o mapa#
La sintaxis para crear mapas o diccionarios en Python es la siguiente:
diccionario_vacio = {}
persona = {
'nombre': 'Juan',
'edad': 25
}Ejemplos de uso#
Los diccionarios son útiles en muchos casos. A continuación se mencionan algunos de ellos.
Objetos y mapeos#
Podemos modelar objetos y entidades con atributos clave-valor:
producto = {
'nombre': 'Smartphone',
'precio': 500,
'marca': 'XYZ'
}Conteos y frecuencias#
Contar ocurrencias de elementos en secuencias:
texto = "Hola mundo mundo"
frecuencias = {}
for palabra in texto.split():
if palabra in frecuencias:
frecuencias[palabra] += 1
else:
frecuencias[palabra] = 1
print(frecuencias)
# {'Hola': 1, 'mundo': 2}Almacenar y acceder a datos#
Como alternativa de alta performance a lists y arrays.
Conclusión#
Los diccionarios son estructuras de datos versátiles gracias a su rápido acceso basado en claves únicas. Tienen usos en casi todos los programas, por lo que dominar diccionarios es indispensable en cualquier lenguaje.
¡Felicitaciones por llegar hasta acá! Espero que este recorrido por el universo de la programación te haya resultado tan interesante como lo fue para mí al escribirlo.
Queremos conocer tu opinión, así que no dudes en compartir tus comentarios, sugerencias y esas ideas brillantes que seguro tenés.
Además, para explorar más allá de estas líneas, date una vuelta por los ejemplos prácticos que armamos para vos. Todo el código y los proyectos los encontrarás en nuestro repositorio de GitHub learn-software-engineering/examples.
Gracias por ser parte de esta comunidad de aprendizaje. ¡Seguí programando y explorando nuevas areas en este fascinante mundo del software!








