La naturaleza LIFO de las pilas se debe a que sólo se puede acceder y manipular el elemento superior. La operación de colocar un elemento sobre la pila se conoce como “push”, mientras que sacar un elemento de la pila es un “pop”. El funcionamiento LIFO provoca que el último elemento colocado en una pila sea el primero en ser retirado.
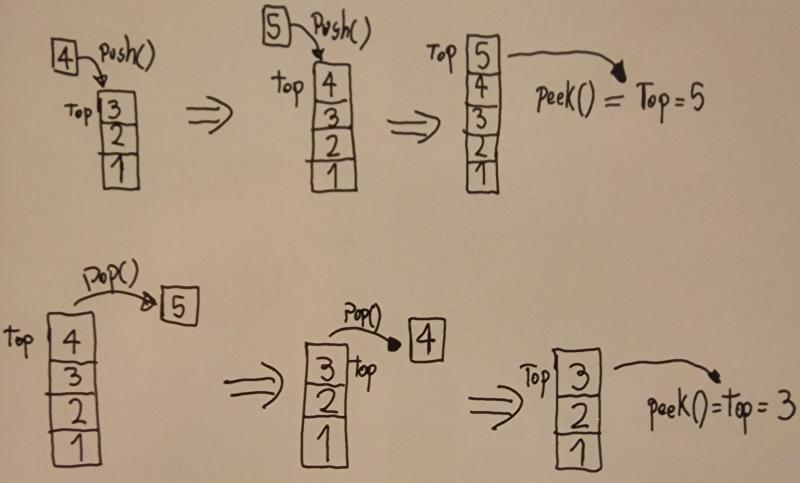
Operaciones principales#
Las operaciones primarias que soporta una estructura de pila son:
- Push: agrega un elemento encima de la pila.
- Pop: saca el elemento de la pila que se encuentra en la cima.
- Peek: permite acceder al elemento de la cima sin sacarlo de la pila.
- isEmpty: consulta si la pila se encuentra vacía.
La mayoría de los lenguajes como Python y Java proveen implementaciones de pilas en sus librerías estándar.
Implementación#
Una pila puede implementarse utilizando una lista enlazada de manera que cada node apunte al nodo anterior.
class Node:
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value
self.previous = None
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.top = None
self.size = 0
def push(self, value):
new_node = Node(value)
if self.top is None:
self.top = new_node
else:
new_node.previous = self.top
self.top = new_node
self.size += 1
def pop(self):
if self.top is None:
return None
top_node = self.top
self.top = self.top.previous
self.size -= 1
return top_node.value
def peek(self):
if self.top is None:
return None
return self.top.value
def is_empty(self):
return self.top is None # Returns true if top is None
def __len__(self):
return self.size
def __str__(self):
values = []
current = self.top
while current:
values.append(str(current.value))
current = current.previous
return "\n".join(values)
print("Creating a new stack")
stack = Stack()
print("==========")
print("Check if stack is empty")
print(f"Is stack empty? {stack.is_empty()}")
print("==========")
print("Push first element")
print(" stack.push(\"First\")")
stack.push("First")
print("==========")
print("Print stack:")
print(stack)
print("==========")
print("Print top element using peek")
print(f"stack.peek() => {stack.peek()}")
print("Add two more elements: stack.push(\"\"):")
print(" stack.push(\"Second\")")
print(" stack.push(\"Third\")")
stack.push("Second")
stack.push("Third")
print("==========")
print("Print stack:")
print(stack)
print("==========")
print("Print top element using peek")
print(f"stack.peek() => {stack.peek()}")
print("==========")
print("Check if stack is empty")
print(f"Is stack empty? {stack.is_empty()}")
print("==========")
print("Get top element using pop")
print(f"stack.pop() => {stack.pop()}")
print("==========")
print("Print top element using peek")
print(f"stack.peek() => {stack.peek()}")
print("==========")
print("Get top element using pop")
print(f"stack.pop() => {stack.pop()}")
print("==========")
print("Get top element using pop")
print(f"stack.pop() => {stack.pop()}")
print("==========")
print("Check if stack is empty")
print(f"Is stack empty? {stack.is_empty()}")Ejemplos de uso#
Las pilas tienen muchos usos en programación:
Pila de ejecución (call stack): registra las llamadas a funciones pendientes de resolver. Implementa el comportamiento LIFO esperado.
Pila de navegador: permite volver atrás (undo) en el historial de navegación de forma similar a una pila LIFO.
Ejecución de expresiones matemáticas: mediante una pila se puede verificar paréntesis, corchetes, llaves, etc.
Algoritmos y estructuras de datos: como en el algoritmo quicksort y en la implementación de buses de datos (datapaths).
Conclusión#
Las pilas son estructuras de datos versátiles gracias a su principio de funcionamiento LIFO. Tener un buen dominio de pilas, sus usos y aplicaciones es esencial en la ciencia de la computación.








