Elegir un lenguaje de programación#
La elección del lenguaje de programación es el primer y quizás el más crucial paso en el proceso de aprendizaje. Hay varios factores a considerar al seleccionar un lenguaje, incluyendo:
- Propósito: ¿Para qué quieres programar? Si es para desarrollo web, JavaScript o PHP podrían ser buenas opciones. Si estás interesado en la ciencia de datos, R o Python podrían ser más adecuados.
- Comunidad: Un lenguaje con una comunidad activa puede ser esencial para los principiantes. Una comunidad vibrante generalmente significa más recursos, tutoriales y soluciones disponibles en línea.
- Curva de aprendizaje: Algunos lenguajes son más fáciles de aprender que otros. Es fundamental elegir uno que coincida con tu nivel de experiencia y paciencia.
- Oportunidades de trabajo: Si estás buscando una carrera en programación, investigar la demanda del mercado para diferentes lenguajes puede ser útil.
Aunque hay muchos lenguajes valiosos y poderosos, para este curso, hemos elegido Python. Este lenguaje es conocido por su simplicidad y legibilidad, lo que lo hace ideal para aquellos que están empezando. Además, Python cuenta con una comunidad activa y una amplia gama de aplicaciones, desde desarrollo web hasta inteligencia artificial1.
Instalación de Python#
Para usuarios de Windows:#
- Descargar el instalador:
- Visita el sitio web oficial de Python en https://www.python.org/downloads/windows/
- Haz clic en el enlace de descarga para la última versión de Python 3.x.
- Ejecuta el instalador:
- Una vez completada la descarga, localiza y ejecuta el archivo instalador
.exe. - Asegúrate de marcar la casilla que dice “Agregar Python al PATH” durante la instalación. Este paso es crucial para hacer que Python sea accesible desde el Símbolo del Sistema.
- Sigue las indicaciones de instalación.
- Una vez completada la descarga, localiza y ejecuta el archivo instalador
- Verifica la instalación:
- Abre el Símbolo del Sistema y escribe:
python --version - Esto debería mostrar la versión de Python que acabas de instalar.
- Abre el Símbolo del Sistema y escribe:
Para usuarios de Mac:#
- Descargar el instalador:
- Visita el sitio web oficial de Python en https://www.python.org/downloads/mac-osx/
- Haz clic en el enlace de descarga para la última versión de Python 3.x.
- Ejecuta el instalador:
- Una vez descargado, localiza y ejecuta el archivo
.pkg. - Sigue las indicaciones de instalación.
- Una vez descargado, localiza y ejecuta el archivo
- Verifica la instalación:
- Abre la Terminal y escribe:
python3 --version - Esto debería mostrar la versión de Python que acabas de instalar.
- Abre la Terminal y escribe:
Para usuarios de Linux (Ubuntu/Debian):#
- Actualiza los paquetes:
sudo apt update - Instala Python:
sudo apt install python3 - Verifica la instalación:
- Después de la instalación, puedes comprobar la versión de Python instalada escribiendo:
python3 --version
- Después de la instalación, puedes comprobar la versión de Python instalada escribiendo:
Entornos de Desarrollo Integrado (IDEs)#
Un IDE es una herramienta que facilita el desarrollo de aplicaciones al combinar comúnmente utilizadas en un solo software: editor de código, compilador, depurador, entre otros. Elegir el IDE adecuado puede hacer que el proceso de programación sea más fluido y eficiente.
Al evaluar IDEs, considera:
- Compatibilidad con el lenguaje: No todos los IDEs son compatibles con todos los lenguajes de programación.
- Características: Algunos IDEs ofrecen funcionalidades como autocompletado, resaltado de sintaxis y herramientas de depuración.
- Extensiones y plugins: La posibilidad de personalizar y extender tu IDE a través de plugins puede ser muy útil.
- Precio: Hay IDEs gratuitos y otros de pago. Evalúa si las características adicionales de un IDE de pago justifican el costo.
Para este curso, hemos seleccionado Visual Studio Code (VS Code). Es un IDE popular que es gratuito y de código abierto. Es conocido por su interfaz sencilla, amplia gama de plugins y capacidad para manejar múltiples lenguajes de programación2. Su comunidad activa garantiza actualizaciones regulares y una amplia gama de recursos de aprendizaje.
Instalación de Visual Studio Code#
Para usuarios de Windows:#
- Descargar el instalador:
- Visita el sitio web oficial de VS Code en https://code.visualstudio.com/
- Haz clic en el botón “Descargar para Windows”.
- Ejecuta el instalador:
- Una vez completada la descarga, localiza y ejecuta el archivo instalador
.exe. - Sigue las indicaciones de instalación, incluyendo aceptar el acuerdo de licencia y elegir la ubicación de instalación.
- Una vez completada la descarga, localiza y ejecuta el archivo instalador
- Inicia VS Code:
- Tras la instalación, puedes encontrar VS Code en tu menú de inicio.
- Lánzalo, ¡y estarás listo para comenzar a programar!
Para usuarios de Mac:#
- Descargar el instalador:
- Visita el sitio web oficial de VS Code en https://code.visualstudio.com/
- Haz clic en el botón “Descargar para Mac”.
- Instala VS Code:
- Una vez descargado, abre el archivo
.zip. - Arrastra la aplicación Visual Studio Code
.appa la carpetaAplicaciones, para que esté disponible en el Launchpad.
- Una vez descargado, abre el archivo
- Inicia VS Code:
- Usa la búsqueda de Spotlight o navega hasta tu carpeta de Aplicaciones para iniciar VS Code.
Para usuarios de Linux (Ubuntu/Debian):#
- Actualiza los paquetes e instala las dependencias:
sudo apt update sudo apt install software-properties-common apt-transport-https wget - **Descarga e instala la claves necesarias:
wget -q https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc -O- | sudo apt-key add - - Añade el repositorio de VS Code:
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://packages.microsoft.com/repos/vscode stable main" - Instala Visual Studio Code:
sudo apt update sudo apt install code - Inicia VS Code:
- Puedes iniciar VS Code desde la terminal escribiendo
codeo encontrarlo en tu lista de aplicaciones instaladas.
- Puedes iniciar VS Code desde la terminal escribiendo
Escribe y ejecuta tu primer programa#
Una vez que hayas configurado tu entorno de programación, es hora de sumergirse en la codificación.
¡Hola mundo!#
Este es posiblemente el programa más icónico para principiantes. Es simple, pero te introduce al proceso de escribir y ejecutar código.
print("¡Hola mundo!")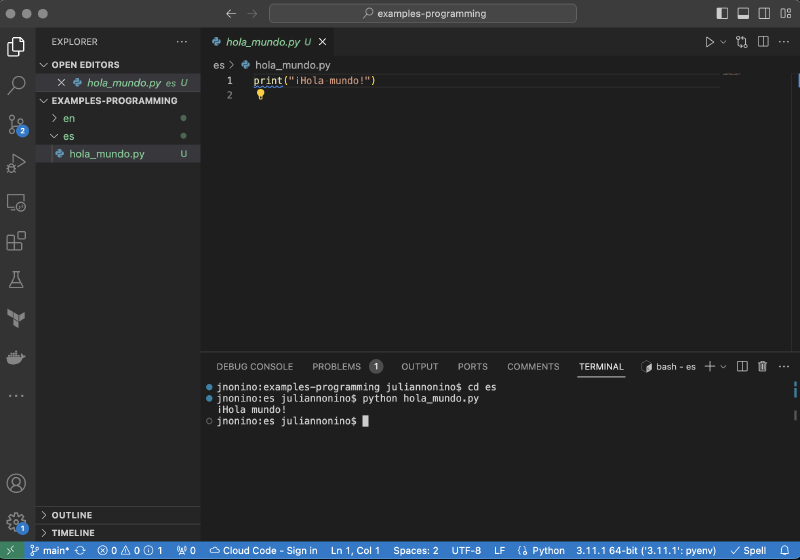
Cálculo de área y perímetro de un triángulo#
Este programa es un poco más complejo. No solo imprime un mensaje, sino que también realiza cálculos matemáticos.
# Entrada del usuario
lado1 = float(input("Introduce la longitud del primer lado: "))
lado2 = float(input("Introduce la longitud del segundo lado: "))
lado3 = float(input("Introduce la longitud del tercer lado: "))
# Cálculo del perímetro
perimetro = lado1 + lado2 + lado3
# Cálculo del área usando la fórmula de Herón
s = perimetro / 2
area = (s*(s-lado1)*(s-lado2)*(s-lado3)) ** 0.5
print(f"El perímetro del triángulo es: {perimetro}")
print(f"El área del triángulo es: {area:.2f}")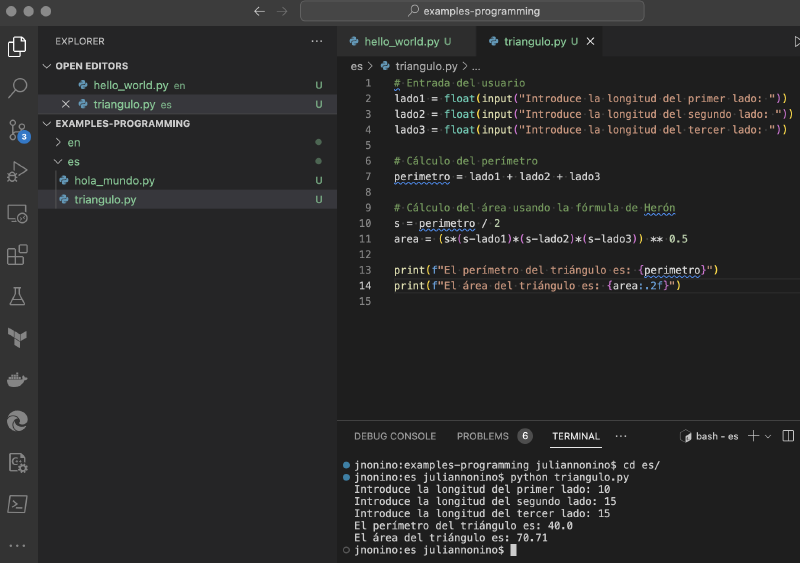
Conclusión#
Configurar un entorno de programación puede parecer desalentador al principio, pero con las herramientas y recursos adecuados, se convierte en una tarea manejable y gratificante. Esperamos que este artículo te haya proporcionado una base sólida para comenzar tu viaje en programación. ¡Feliz codificación!
¡Gracias por haber llegado hasta acá!
Si te gustó el artículo, por favor ¡no olvides compartirlo con tu familia, amigos y colegas!
Y si puedes, envía tus comentarios, sugerencias, críticas a nuestro mail o por redes sociales, nos ayudarías a generar mejor contenido y sobretodo más relevante para vos.





